Non Linear Data structures – trees
Tree is a data structure that stores element in a hierarchy.
Root – Top node of tree
Root is parent of its children.
Each node can have up to two nodes…this is called a binary tree.
Trees
– represent hierarchical data
– databases
– autocompletion
– compilers (syntax tree to parse expressions)
– compression (JPEG, MP3)
left < node < right At every step of comparison, we throw away half of the tree. This is what we call Logarithmic Time
Lookup
O(log n)
Inserting node
Finding a Node O(log n) + Inserting Node O(1) = O(log n)
Delete Node
O(log n)
Depth First Search (DFS)
pre-order – (left of node)
in-order – (bottom of node) ascending order
post-order – (right of node)
Breadth First – Level by level (BFS)
Recursion
Iteration – loops.
Recursion – no loops.
Base condition terminates Recursion.
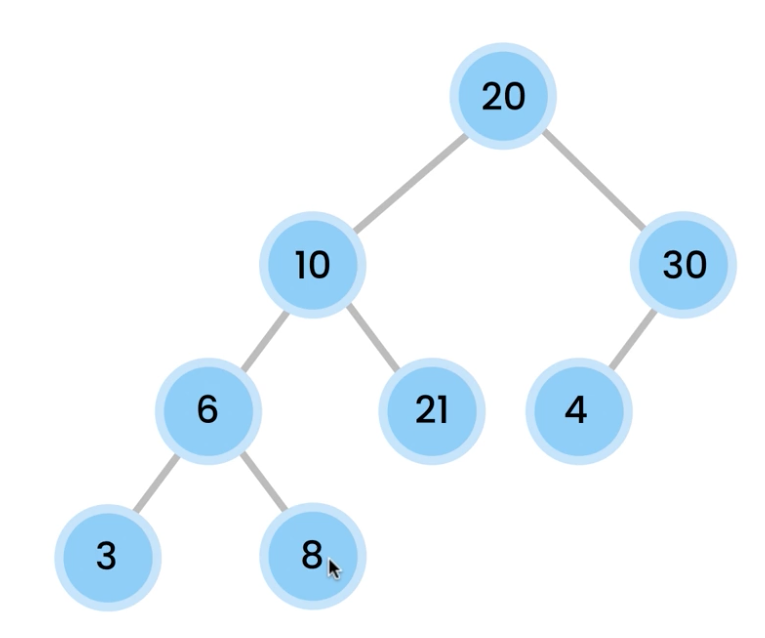
Depths and Height
Depths starts at the root
Depths of root is 0. As it goes deeper, it increases.
Depth of 10 is 1.
Depth of 21 is 2.
Depth of 8 is 3.
Depth – # of edges from root to target node.
Height is opposite of depth.
Height starts at the leaf
Height of leafs are 0.
As we go up, height increases. Longest path from target node to leaf.
Height of 6 is 1.
Height of 30 is 1.
Height of 10 is 2. We actually have 3 different paths. 3 to 10. 8 to 10. 21 to 10. Longest path is 2.
Height of 20 is 3, because it’s the longest path.
1 + max(height(L) + height(R))
Post Traversal – visit all leaves first
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
function getHeight() { if (!root) return 0; return height(root); } // private height(node) { if (!node.left && !node.right) { return 0; } return 1 + Math.max( height(node.left), height(node.right)); } |
Find minimum value in BST
If it’s a standard BST, use recursion, and get leftmost leaf.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
function min(node) { // O(log n) if (!node.left) { return node.value; } else { return min(node.left); } } |
But if its NOT a BST, values are all over the place, so
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
function min (node) { // O(n) if (!node) return 0; if (!node.left && !node.right) return node.value; let childrenMin = Math.min(node.left, node.right); return Math.min(childrenMin, node.value); } |
Exercises
– height of tree. return Math.max of left subtree and right subtree. That way, you get the height at the root.
– # of nodes at distance k. simple pre-order and print.
– isBST? pass in parameter min, max. Make sure node value stays within range. If not, false. Kick off with -Infinity and +Infinity.
Minimum – isBST? if yes, get leftmost. If not, then must have parameter reference and recurse down, do compare with every value.
Maximum – isBST? if yes, get rightmost. If not, then must have parameter reference and recurse down, do compare with every value.
– Are the two tree equal (Equality Check)?
– traverse BST (Level Order Traversal)
for i to height of tree
let arr = getNodesAtDistance(i)
for j to arr.length
log arr[j];
Additional exercises
1- Implement a method to calculate the size of a binary tree. Solution: Tree.size()
2- Implement a method to count the number of leaves in a binary tree. Solution: Tree.countLeaves()
4- Implement a method to check for the existence of a value in a binary tree using recursion. Compare this method with the find() method. The find() method does the same job using iteration. Solution: Tree.contains()
5- Implement a method to check to see if two values are siblings in a binary tree. Solution: Tree.areSibling()
6- Implement a method to return the ancestors of a value in a List
SOLUTION
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 |
class Node { constructor(newData, newLeft, newRight) { this.left = newLeft; this.right = newRight; this.data = newData; } print = () => { console.log(this.data); } } class Tree { constructor() { var root = null; this.getRoot = function() {return root;} this.addData = function (data) { if (root == null) { root = new Node(data, null, null); } else { _addNode(root, new Node(data, null, null)); } } function _addNode(node, toAddNode) { if (node == null) { return toAddNode;} if (toAddNode.data > node.data) { node.right = _addNode(node.right, toAddNode); } else { node.left = _addNode(node.left, toAddNode); } return node; } this.printInOrder = function() { console.log(`-- printing nodes in order --`); if (root==null) { console.log('nothing in tree'); } else { _inOrderTraversal(root, function(node){ node.print(); }); } console.log(`-----------------------------`); } function _inOrderTraversal(node, callback) { if (node == null) return; _inOrderTraversal(node.left, callback); callback(node); _inOrderTraversal(node.right, callback); } this.getHeightOfTree = function() { // return Math.max of left subtree and right subtree. // That way, you get the height at the root. if (!root) return 0; return height(root); } function height(node) { // base case if (!node.left && !node.right) return 0; let heightOfLeft = (node.left) ? 1+height(node.left) : 0; let heightOfRight = (node.right) ? 1+height(node.right) : 0; return Math.max(heightOfLeft, heightOfRight); } // isBST? pass in parameter min, max. Make sure node value stays within range. // If not, false. Kick off with -Infinity and +Infinity. this.isBST = function() { return nodeWithMinMax(-Infinity, root, Infinity); } function nodeWithMinMax(smallerValue, node, largerValue) { if (!node) { return true; } // base case let bLeft = nodeWithMinMax(smallerValue, node.left, node.data); let bRight = nodeWithMinMax(node.data, node.right, largerValue); return bLeft && bRight && (node.data > smallerValue && node.data < largerValue); } // used to make a Binary Tree that is not ordered (non-BST) this.errorTree = function () { let Three = new Node(1, null, null) let Eleven = new Node(11, null, Three) let Two = new Node(2, null, null); root = new Node(99, new Node(12, Two, null), Eleven); } // Nodes at K distance. Given distance from the root. // print all nodes with distance 3 from root. You print the nodes. Not the whole subtree. this.nodesWithKDistanceFromRoot = function(k) { let queue = []; distanceK(root, 0, k, queue); return queue; } function distanceK(node, count, k, queue) { if (node == null) {return;} if (count == k) { //node.print(); queue.push(node); return; } distanceK(node.left, count+1, k, queue); distanceK(node.right, count+1, k, queue); } // Minimum – isBST? if yes, get leftmost. If not, then must have parameter reference and recurse down, do compare with every value. this.getMinimumValue = function() { if (this.isBST()) { return getLeftMostNode(root).data; } else { return getMinInNonBST(root, Infinity); } } function getLeftMostNode(node) { return (node.left) ? getLeftMostNode(node.left) : node; } function getMinInNonBST(node, min) { if (!node) return Infinity; min = Math.min(node.data, min); if (!node.left && !node.right) return min; return Math.min(getMinInNonBST(node.left, min), getMinInNonBST(node.right, min)); } this.getMaximumValue = function() { if (this.isBST()) { return getRightMostNode(root).data; } else { return getMaxInNonBST(root, -Infinity); } } function getRightMostNode(node) { return (node.right) ? getRightMostNode(node.right) : node; } function getMaxInNonBST(node, max) { if (!node) return -Infinity; max = Math.max(node.data, max); if (!node.left && !node.right) return max; return Math.max(getMaxInNonBST(node.left, max), getMaxInNonBST(node.right, max)); } this.getBSTatLvl = function(level) { for (let i = 0; i <= level; i++) { let q = this.nodesWithKDistanceFromRoot(i); console.log(`-- Depth of ${i} --`); q.forEach(item => console.log(item.data)); } } this.getLeaves = function() { // done let ht = this.getHeightOfTree(root); return this.nodesWithKDistanceFromRoot(ht); } this.treeSize = function() { // done let ht = this.getHeightOfTree(root); let total = []; for (let i = 0; i <= ht; i++) { let q = this.nodesWithKDistanceFromRoot(i); total = total.concat(q); } return total.length; } this.findValue = function(value, callback) { // done return checkValue(root, value, callback); } function checkValue(node, value, callback) { if (!node) return null; else if (node.data == value) { callback(node); return node; } let left = checkValue(node.left, value, callback); let right = checkValue(node.right, value, callback); return (left || right); } this.areSiblings = function(first, second) { // done return checkSib(root, first, second) } function checkSib(node, first, second) { if (!node.left || !node.right) { return false } let bChildren = checkSib(node.left, first, second) || checkSib(node.right, first, second); if (node.left && node.right) { return (node.left.data == first && node.right.data == second) || bChildren; } return bChildren; } function f(node, value, ancestorList) { if (!node) {return false;} if (node && (node.data === value)) { // when found, we immediately return true return true; } else { // if not found, we recruse down let left = f(node.left, value, ancestorList); // we check if it is an ancestor. If so, we add to the list if (left) { ancestorList.push(node); return true; } let right = f(node.right, value, ancestorList); // we check if it is an ancestor. If so, we add to the list if (right) { ancestorList.push(node); return true; } // if not ancestor, return false, which means don't add to list. return false; } } this.getAncestors = function(value) { let ancestors = []; f(root, value, ancestors); return ancestors; } } // constructor // prototype functions } |
Test
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
let t = new Tree(); t.addData(10); t.addData(8); t.addData(9); t.addData(12); t.addData(11); t.addData(7); t.printInOrder(); //t.errorTree(); console.log(`Minimum value in tree is: `, t.getMinimumValue()); console.log(`Maximum value in tree is: `, t.getMaximumValue()); t.getBSTatLvl(2); console.log('Leaves of the tree: ', t.getLeaves()); console.log('treeSize: ' + t.treeSize()); // find value in tree. If exists, return node let toFind = 8; let foundNode = t.findValue(toFind, function(node) { console.log(`callback way: found ${toFind}`, node); }); console.log(`return way: found ${toFind}`, foundNode); // are two values siblings? let valueOne = 8; let valueTwo = 12; console.log(`Are ${valueOne} and ${valueTwo} siblings?`, t.areSiblings(valueOne, valueTwo)); // get ancestors of a value let ancestorsOfValue = 11; let ancestorsArr = t.getAncestors(ancestorsOfValue); console.log(`ancestors of ${ancestorsOfValue}: `, ancestorsArr); |